| Molecular Formula: | C388H636N106O119S |
| Molecular Weight: | 8722.2 |
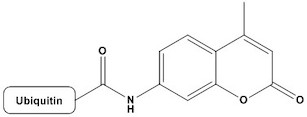
| Ubiquitin-AMC (Ubiquitin-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin) is a fluorogenic substrate widely used in biochemical assays to study the activity of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs). DUBs are proteases that cleave ubiquitin from proteins, and Ubiquitin-AMC serves as a sensitive tool to measure their enzymatic activity. Below is a detailed review of Ubiquitin-AMC, including its properties, applications, and considerations: Ubiquitin-AMC consists of ubiquitin, a small regulatory protein, conjugated to a fluorogenic AMC (7-amido-4-methylcoumarin) group. When DUBs cleave the amide bond between ubiquitin and AMC, the released AMC fluoresces, allowing for real-time monitoring of enzyme activity. 1. Chemical Structure (1). Ubiquitin: A 76-amino acid protein involved in post-translational modification, signaling, and protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. (2). AMC (7-amido-4-methylcoumarin): A fluorogenic group that emits blue fluorescence (λₑₘ = 460 nm) when excited at 380 nm. AMC is non-fluorescent when conjugated to ubiquitin but becomes highly fluorescent upon cleavage. (3). Ubiquitin-AMC Bond: The amide bond between the C-terminus of ubiquitin and the AMC group is specifically cleaved by DUBs. 2. Properties (1). Fluorogenic Nature: Ubiquitin-AMC is non-fluorescent in its intact form but becomes fluorescent upon cleavage by DUBs, making it a highly sensitive substrate for enzyme activity assays. (2). Excitation/Emission: Excitation wavelength: 380 nm; Emission wavelength: 460 nm (3). Solubility: Ubiquitin-AMC is soluble in aqueous buffers, making it suitable for enzymatic assays in physiological conditions. (4). Stability: The substrate is stable when stored at -20°C or below, but repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided to prevent degradation. 3. Applications (1). DUB Activity Assays: Ubiquitin-AMC is widely used to measure the activity of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) in vitro. The increase in fluorescence intensity is proportional to DUB activity. (2). High-Throughput Screening (HTS): The fluorogenic nature of Ubiquitin-AMC makes it ideal for screening DUB inhibitors or activators in drug discovery and development. (3). Kinetic Studies: Ubiquitin-AMC allows for real-time monitoring of DUB activity, enabling the determination of kinetic parameters such as KmKm and VmaxVmax. (4). Mechanistic Studies: Researchers use Ubiquitin-AMC to study the mechanisms of DUBs, including substrate specificity, catalytic efficiency, and regulation. (5). Biochemical Research: Ubiquitin-AMC is used to investigate the role of DUBs in cellular processes such as protein degradation, DNA repair, and immune signaling. 4. Advantages (1). High Sensitivity: The fluorogenic nature of Ubiquitin-AMC provides a highly sensitive readout for DUB activity, even at low enzyme concentrations. (2). Real-Time Monitoring: The assay allows for continuous, real-time measurement of enzyme activity, enabling kinetic analysis. (3). Versatility: Ubiquitin-AMC can be used with a wide range of DUBs, including ubiquitin- specific proteases (USPs), ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs), and ovarian tumor proteases (OTUs). (4). Compatibility: The substrate is compatible with standard fluorescence plate readers and high-throughput screening systems. 5. Limitations (1). Substrate Specificity: While Ubiquitin-AMC is cleaved by many DUBs, some enzymes may exhibit low activity or specificity toward this substrate. (2). Fluorescence Interference: Compounds or proteins in the assay mixture that absorb or emit light near 380 nm or 460 nm may interfere with the fluorescence signal. (3). Storage and Handling: Ubiquitin-AMC should be stored at -20°C or below and protected from light to prevent degradation. Repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided. 6. Comparison with Other DUB Substrates (1). Ubiquitin-Rhodamine 110: A fluorogenic substrate with higher fluorescence intensity but different excitation/emission wavelengths (λₑₓ = 485 nm, λₑₘ = 535 nm). (2). Ubiquitin-AFC (7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin): A fluorogenic substrate with similar properties but different fluorescence characteristics. (3). Ubiquitin-VS (Ubiquitin-vinyl sulfone): A non-fluorogenic, irreversible inhibitor used for DUB profiling. Among these, Ubiquitin-AMC is the most widely used due to its balance of sensitivity, compatibility, and ease of use. Ubiquitin-AMC is a powerful and versatile tool for studying deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs). Its fluorogenic nature, high sensitivity, and compatibility with real-time assays make it a preferred choice for DUB activity measurements, high-throughput screening, and mechanistic studies. However, its cost, potential for fluorescence interference, and storage requirements should be considered when designing experiments. Overall, Ubiquitin-AMC is an indispensable reagent for researchers studying the ubiquitin-proteasome system and DUB biology. References 1. Ub-AMC 2. Efficient semi-synthesis of ubiquitin-7-amino-4-methylcoumarin 3. Chemical synthesis of Ub-AMC via ligation of peptide hydrazides 4. Characterization of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like-protein isopeptidase activities 5. Competition Assay for Measuring Deubiquitinating Enzyme Substrate Affinity 6. Ubiquitin binding proteins protect ubiquitin conjugates from disassembly 7. Targeting ubiquitin specific proteases (USPs) in cancer immunotherapy: from basic research topreclinical application 8. Phosphorylation and activation of ubiquitin-specific protease-14 by Akt regulates the ubiquitin-proteasome system |
|
Ubiquitin-AMC
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.