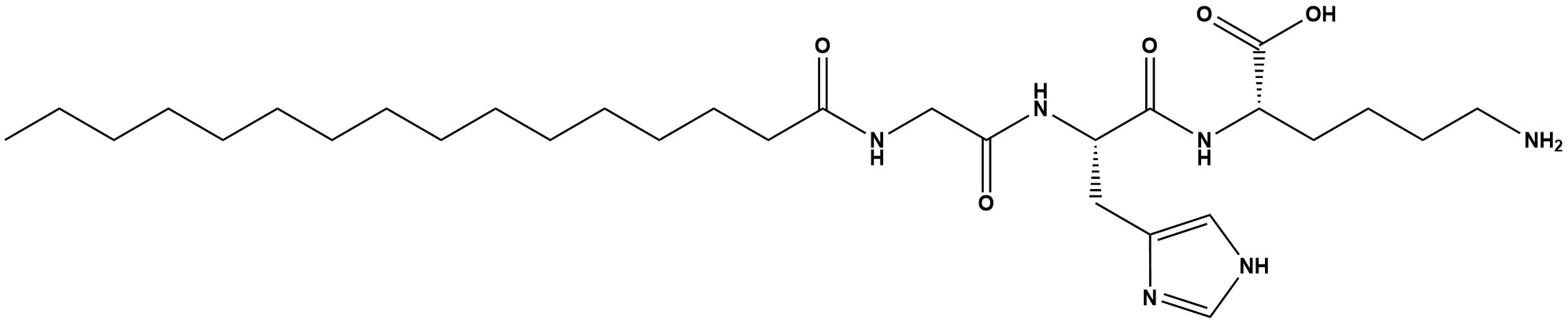
| Synonym: | Pal-GHK; Palmitoyl Oligopeptide |
| Sequence: | Pal-Gly-His-Lys |
| CAS #: | 147732-56-7 |
| Molecular Formula: | C30H54N6O5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 578.8 |
| Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 (Pal-GHK), also known as Palmitoyl-Gly-His-Lys, is a lipophilic tripeptide derived from the naturally occurring copper-binding peptide Glycyl-Histidyl-Lysine (GHK). Developed in the late 20th century and popularized by Sederma (part of Croda International), Pal-GHK consists of a palmitic acid chain attached to the N-terminus of the GHK sequence. This modification enhances its lipophilicity, improving skin penetration compared to the hydrophilic GHK peptide. With a molecular weight of approximately 578 Da, Pal-GHK is celebrated for stimulating collagen production, promoting wound healing, and reducing visible signs of aging, making it a staple in anti-wrinkle creams, serums, and repair-focused skincare formulations. 1. Chemical and Physical Properties Pal-GHK is a synthetic tripeptide with the structure Palmitoyl-Gly-His-Lys, where palmitic acid (C16H32O2) is conjugated to the N-terminal glycine via an amide bond. The sequence Gly-His-Lys mimics a fragment of the alpha-1 chain of type I collagen, a key structural protein in skin. The palmitoyl group increases its logP value (lipophilicity), allowing better diffusion through the stratum corneum compared to unmodified GHK (logP < 0). Pal-GHK appears as a white to off-white powder, soluble in oils and organic solvents like ethanol, but less so in water, necessitating emulsified or lipid-based formulations for cosmetic use. The peptide is stable under neutral to slightly acidic pH (4.5–7.0) and typical storage conditions (cool, dry environments), though it may degrade under extreme heat, UV exposure, or highly alkaline conditions. Its small size and amphiphilic nature make it an effective bioactive ingredient when properly formulated. 2. Mechanism of Action Pal-GHK exerts its effects through multiple biological pathways, primarily by mimicking the activity of GHK, a peptide known for copper chelation and extracellular matrix (ECM) modulation: 2.1 Collagen and ECM Stimulation: • Pal-GHK upregulates the synthesis of collagen (types I and III) and other ECM components like glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and fibronectin by signaling fibroblasts via cell surface receptors. Studies suggest it activates transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) pathways, a key regulator of collagen production. • It mimics the natural breakdown fragments of collagen, “tricking” the skin into repairing perceived damage, thus enhancing firmness and elasticity. 2.2 Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects: • By chelating copper ions, Pal-GHK reduces oxidative stress, neutralizing free radicals that degrade collagen and elastin. This parallels GHK’s role in wound healing and tissue repair. • It downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6), mitigating inflammation linked to aging and UV damage. 2.3 Wound Healing and Tissue Repair: • Pal-GHK accelerates keratinocyte and fibroblast proliferation, promoting re-epithelialization and ECM remodeling, a property inherited from GHK’s documented effects in dermal repair. Unlike neurotransmitter-inhibiting peptides like Acetyl Hexapeptide-8, Pal-GHK targets structural aging rather than dynamic wrinkles, making it a complementary rather than competitive ingredient in anti-aging formulations. 3. Applications 3.1 Cosmetic Anti-Aging: • Wrinkle Reduction: Pal-GHK is used in creams and serums to reduce fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen and improving skin thickness. Clinical trials report up to 36% wrinkle depth reduction after 4 weeks at 3 ppm (parts per million) concentration. • Skin Firmness: It enhances elasticity and firmness, countering sagging associated with chronological aging and photoaging. • Moisturization Support: By increasing GAGs like hyaluronic acid, it improves skin hydration and plumpness. 3.2 Post-Procedure Care: • Pal-GHK is incorporated into post-peel or microneedling products to accelerate healing, reduce redness, and restore barrier function, leveraging its wound-healing properties. 3.3 Hair Growth Stimulation: • Emerging research suggests Pal-GHK may promote hair follicle health by stimulating dermal papilla cells, though this application remains less developed than its skincare uses. 3.4 Therapeutic Potential: • Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects hint at broader applications, such as in scar reduction or managing chronic skin conditions, though clinical evidence is limited. 4. Advantages • Enhanced Penetration: The palmitoyl group improves delivery through the skin’s lipid barrier, outperforming unmodified GHK in topical applications. • Multifaceted Benefits: It addresses multiple aging signs—wrinkles, sagging, and oxidative damage—making it a versatile ingredient. • Safety Profile: Pal-GHK is well-tolerated, with no significant toxicity (LD50 > 2000 mg/kg) or irritation reported in patch tests, as per Cosmetic Ingredient Review assessments. • Synergy: It pairs effectively with other actives like retinoids, vitamin C, or peptides (e.g., Palmitoyl Tetrapeptide-7) for comprehensive anti-aging regimens. • Subtle, Long-Term Effects: Unlike instant fillers, Pal-GHK offers gradual, natural improvements, appealing to users seeking sustainable results. 5. Limitations • Slow Onset: Effects require 4–12 weeks of consistent use, lacking the immediacy of injectables or neurotoxin mimics. • Concentration Dependence: Efficacy peaks at low concentrations (3–10 ppm); higher doses yield diminishing returns and may destabilize formulations. • Penetration Variability: While more lipophilic than GHK, Pal-GHK’s delivery still depends on formulation quality (e.g., emulsions, liposomes), with inconsistent results in poorly designed products. • Limited Clinical Data: While in vitro and small-scale studies support its benefits, large-scale, peer-reviewed human trials are sparse, leading to some skepticism about potency. • Cost: High-purity Pal-GHK is expensive to synthesize, increasing the price of premium formulations. 6. Delivery and Optimization To maximize efficacy, formulation strategies focus on improving bioavailability: • Liposomes and Emulsions: Encapsulation in liposomes or water-in-oil emulsions enhances penetration and stability, with studies showing up to 50% greater collagen stimulation in liposomal forms. • Combination with Penetration Enhancers: Ingredients like dimethyl isosorbide or oleic acid boost delivery through the stratum corneum. • Nanoemulsions: Recent advancements use nanoemulsions to reduce particle size, improving absorption and uniformity in skin application. • pH Optimization: Formulations at pH 5–6 maintain stability and compatibility with skin’s natural acidity. 7. Comparison with Alternatives • vs. GHK Peptide: Pal-GHK’s lipid modification enhances penetration and efficacy over native GHK, though GHK-Cu (copper-bound) may have stronger wound-healing effects. • vs. Acetyl Hexapeptide-8: Pal-GHK targets structural aging (collagen loss) while AH-8 addresses dynamic wrinkles (muscle activity), making them complementary. • vs. Retinoids: Retinoids offer broader anti-aging benefits (e.g., cell turnover, pigmentation) but are more irritating; Pal-GHK is gentler but less potent. • vs. Palmitoyl Pentapeptide-4 (Matrixyl): Both stimulate collagen, but Pal-GHK acts via GHK mimicry, while Matrixyl mimics a different collagen fragment, offering slightly varied ECM effects. Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 (Pal-GHK) is a highly effective, science-backed peptide for anti-aging, collagen stimulation, and skin repair. Its lipophilic modification enhances penetration, setting it apart from its natural GHK predecessor, while its gentle profile broadens its appeal. Though slower-acting and less potent than retinoids or injectables, Pal-GHK excels in long-term skin repair and firmness, particularly when optimized with advanced delivery systems. As research explores new applications (e.g., hair growth) and sustainable production, Pal-GHK remains a versatile, scientifically grounded ingredient in the evolving landscape of cosmeceuticals. References 1. Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 2. Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 | Pal-GHK |
|
Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.