| Synonym: | 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane-1,4-bis-tert-butyl acetate-7-acetic acid |
| CAS #: | 1161415-28-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C20H37N3O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 415.5 |
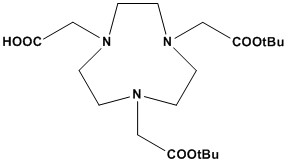
| NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester) (CAS #: 1161415-28-6) is a highly valuable bifunctional chelator widely used in radiopharmaceutical chemistry, particularly for developing targeted radiopharmaceuticals for molecular imaging (PET/SPECT) and radionuclide therapy. It is a derivative of the macrocyclic chelator NOTA (1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid), distinguished by its smaller ring size (9-membered) compared to DOTA (12-membered) and its specific protection strategy. 1. Chemical Structure and Properties • Core Macrocycle: The fundamental structure of NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester) is the NOTA macrocycle (1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid). This nine-membered cyclic triamine features three acetic acid pendant arms. The smaller ring size and fewer nitrogen atoms (three vs. four in DOTA) are key differentiating features that influence its metal chelation properties. • Protection Strategy: In NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester), two of the three carboxylic acid groups on the acetic acid arms are protected as tert-butyl esters (t-Bu ester). Crucially, the third carboxylic acid group remains free (unprotected). • tert-Butyl Ester: Similar to DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester), the tert-butyl ester is an acid-labile protecting group, easily removed under mild acidic conditions (e.g., trifluoroacetic acid, TFA). This selective protection allows for targeted functionalization at the free carboxylic acid while preventing unwanted reactions at the other two. • Solubility: Generally soluble in common organic solvents such as DMSO, methanol, and ethanol. It also shows some solubility in PBS (pH 7.2). This facilitates its use in various synthetic coupling reactions. • Bifunctional Nature: The combination of a metal-chelating macrocyclic core and a selectively addressable free carboxylic acid (or its activated derivatives, such as an NHS ester) makes NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester) a bifunctional chelator. This design enables it to both bind a metal ion stably and covalently attach to a biomolecule. 2. Applications NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester) is a key reagent in the burgeoning field of nuclear medicine, primarily for the development of targeted radiopharmaceuticals. 2.1 Radiopharmaceutical Development NOTA is known for its strong binding affinity to metals such as: • Gallium-68 (⁶⁸Ga): Widely used in PET imaging agents. • Copper-64 (⁶⁴Cu) and Zirconium-89 (⁸⁹Zr): Important for diagnostic and theranostic applications. The bis(t-Bu ester) protection allows for easier synthetic handling, and once conjugated to biomolecules (antibodies, peptides), the ester groups can be removed to regenerate the active chelating form for metal complexation. 2.2 Bioconjugation • The free carboxylic acid group of NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester) serves as the versatile attachment point for covalently linking the chelator to various targeting biomolecules. This can be achieved through standard amide bond formation (e.g., reaction with primary amines on peptides via EDC/NHS coupling) or by converting it to other reactive intermediates (e.g., NOTA-NHS ester, maleimide-NOTA) to react with different functional groups on biomolecules. • This bioconjugation step allows for the creation of specific radiopharmaceuticals that target disease-specific receptors or biomarkers, improving diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic targeting. 2.3 Chemical Synthesis • It acts as a key intermediate in the synthesis of a wide range of NOTA-based conjugates with diverse functionalities, including those with additional linkers (e.g., PEGylation for altered pharmacokinetics) or other reactive groups for advanced chemical modifications. 3. Advantages over DOTA (for certain applications) While DOTA is a highly versatile chelator, NOTA (and its derivatives like NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester)) offers specific advantages for certain applications, particularly with Gallium-68: • Faster Radiolabeling Kinetics: NOTA complexes with Gallium-68 significantly faster than DOTA, often at room temperature or with minimal heating. This is crucial for short-lived radionuclides like Gallium-68 (half-life ~68 min) and for preserving the integrity of temperature-sensitive biomolecules. • Higher Kinetic Stability for some metals: For certain metals (e.g., Copper-64), NOTA has shown superior in vivo kinetic stability compared to DOTA, leading to less in vivo demetallation and reduced off-target accumulation (e.g., lower liver uptake for Copper-64-NOTA vs. Copper-64-DOTA). • Smaller Size: The smaller macrocyclic ring of NOTA can sometimes lead to less steric hindrance when conjugated to biomolecules, potentially affecting receptor binding or pharmacokinetics favorably in some cases. • Versatility for Fluorine-18-AlF: Its compatibility with the robust and efficient Fluorine-18-AlF labeling method provides a significant advantage for Fluorine-18-based radiopharmaceuticals. NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester) (CAS #: 1161415-28-6) is an indispensable bifunctional chelator in the development of cutting-edge radiopharmaceuticals. Its defining features – the NOTA macrocycle with two protected and one free carboxylic acid – make it uniquely suited for rapid and efficient radiolabeling, especially with short-lived positron emitters like Gallium-68, and for stable conjugation to targeting biomolecules. Its advantages in kinetics and stability for certain metals, particularly over DOTA in some contexts, position it as a preferred choice for many diagnostic imaging and theranostic applications in modern nuclear medicine. Its continued utility underscores the importance of tailored chelator design for optimized radiopharmaceutical performance. |
|
NOTA-bis(t-Bu ester)
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.