| CAS #: | 1887132-90-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | C18H15F5N2O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 450.3 |
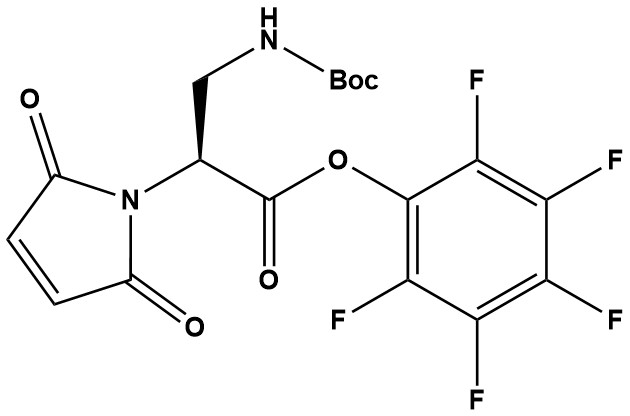
| Mal-Dap(Boc)-OPfp (CAS 1887132-90-2) is a highly specialized, pre-activated amino acid derivative designed for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS). It serves as a potent building block for introducing a maleimide functionality at the N-terminus of a peptide sequence. This reagent creates a bridge between peptide chemistry and bioconjugation. By incorporating the maleimide group directly during the synthesis phase (rather than as a post-synthesis modification), it significantly improves yield and purity, reducing the complexity of preparing maleimide-functionalized peptides. 1. Functional Architecture The power of this reagent lies in its three distinct functional components, each serving a specific role in the synthesis pipeline: 1.1 The Activated Ester (OPfp) Unlike standard amino acids that often require on-the-spot activation (using HATU/DIC), this molecule comes as a Pentafluorophenyl (OPfp) ester. • Why OPfp? Pfp esters are highly reactive toward primary amines but are generally more stable to hydrolysis than NHS esters during handling. • Benefit: This ensures extremely rapid and high-yielding coupling to the -terminus of the resin-bound peptide, which is critical when attaching bulky functional groups. 1.2 The Maleimide Head (Mal) The α-amino group of the Dap backbone is already converted into a Maleimide. • Role: This acts as the “warhead” for downstream bioconjugation. • Stability: Because the maleimide is pre-formed, there is no risk of cross-linking or polymerization during the coupling step, provided the peptide lacks free thiols. • Limitation: Since the α-amine is consumed by the maleimide ring, this unit terminates the peptide chain at the N-terminus. No further amino acids can be added to the α-position. 1.3 The Side-Chain Protection (Boc) The β-amine of the Dap side chain is protected with a (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) group. • Role: Prevents side reactions during the coupling of the reagent to the peptide. • Deprotection: The group is acid-labile. It is typically removed during the final TFA cleavage step of the peptide from the resin. • Result: Upon cleavage, the side chain becomes a free primary amine (-NH2). This increases the hydrophilicity of the linker or offers a secondary site for modification if orthogonal protection strategies are used. 2. Primary Applications 2.1 Peptide-Drug Conjugates (PDCs) & ADCs This is the standard reagent for creating “Maleimide-Peptide” linkers. • Workflow: Synthesize the peptide on resin Cap with Mal-Dap(Boc)-OPfp Cleave (removing Boc) Conjugate to a Drug or Antibody via the Maleimide. 2.2 Dual-Functional Linkers Because the final product contains both a Maleimide (thiol-reactive) and a Side-Chain Amine (from the deprotected Dap), this reagent allows for the creation of heterobifunctional peptide linkers. • The Maleimide can react with a Cysteine on an antibody. • The side-chain Amine can be reacted with an NHS-ester drug payload or fluorophore. 2.3 Improving Solubility The Dap (Diaminopropionic acid) backbone is relatively short and, once deprotected, positively charged (depending on pH). This can help improve the aqueous solubility of hydrophobic peptide payloads compared to using simple hydrocarbon spacers. 3. Advantages Over Traditional Methods Method A (Traditional): Synthesize Peptide→React N-terminus with a crosslinker like SMCC. • Downside: SMCC can be expensive, the reaction requires strict pH control, and purification is often needed to remove excess crosslinker. Method B (Using Mal-Dap(Boc)-OPfp): • Efficiency: The maleimide is installed as just another amino acid coupling step. • Purity: Excess reagent is washed away while the peptide is still on the solid phase (resin), eliminating a difficult purification step later. • Cost-Effective: Reduces the number of post-cleavage synthetic steps. 4. Handling and Storage • Moisture Sensitivity: As an activated Pfp ester, the reagent is sensitive to hydrolysis. It must be stored desiccated at -20°C. • Solubility: Soluble in common SPPS solvents like DMF (Dimethylformamide), DCM (Dichloromethane), and NMP. • Reaction Conditions: Standard SPPS protocols apply. However, avoid using nucleophilic bases (like Piperidine) after this unit has been coupled, as prolonged exposure to strong bases can degrade the maleimide ring. Since this is a capping reagent, it is added at the very end of the synthesis, avoiding this issue. Mal-Dap(Boc)-OPfp is a sophisticated chemical tool at the intersection of peptide chemistry, bioconjugation, and targeted therapeutics. Its unique combination of a self-hydrolyzing maleimide, activated ester, and protected amino functionality makes it particularly valuable for constructing stable antibody-drug conjugates with improved pharmacological properties. |
|
Mal-Dap(Boc)-OPfp
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.