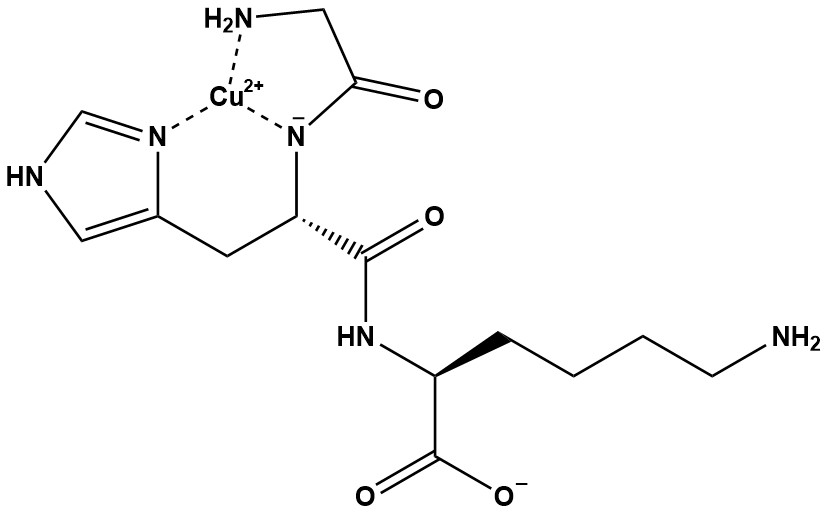
| Synonym: | Copper Tripeptide-1; Prezatide copper |
| Sequence: | Gly-His-Lys-Cu |
| CAS #: | 89030-95-5 |
| Molecular Formula: | C14H22CuN6O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 401.9 |
| GHK-Cu (Glycyl-Histidyl-Lysine-Copper) is a naturally occurring copper-binding peptide with powerful regenerative and anti-aging properties. Discovered in human plasma by Loren Pickart in 1973, it plays a crucial role in wound healing, collagen synthesis, and skin rejuvenation. Often called “Copper Peptide”, it has gained popularity in skincare for its ability to repair damaged tissue, stimulate collagen, and improve skin elasticity. 1. Chemical and Physical Properties GHK-Cu consists of the tripeptide Glycyl-Histidyl-Lysine (GHK) chelated to a Cu²⁺ ion, typically in a 1:1 molar ratio. The copper binds via the histidine imidazole ring, the peptide backbone, and deprotonated amide nitrogens, forming a stable, square-planar coordination complex. This structure gives GHK-Cu a characteristic blue hue in solution, with an absorption peak at 610–630 nm. The peptide is water-soluble (logP < 0) but poorly lipophilic, limiting passive skin penetration without formulation aids. GHK-Cu is stable at physiological pH (6.5–7.5) but dissociates below pH 4 or above pH 9, releasing free copper, which can be pro-oxidant if unbound. Its small size and copper-binding affinity underpin its bioactivity, distinguishing it from larger proteins or synthetic peptides. 2. Mechanism of Action GHK-Cu exhibits a multifaceted mechanism, influencing gene expression, cellular signaling, and copper homeostasis: 2.1 Collagen and ECM Stimulation: • GHK-Cu upregulates genes for collagen (types I, III, IV, VII), elastin, and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) by modulating transcription factors like SP1 and TGF-β. • It also inhibits matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes that degrade ECM, preserving skin structure. 2.2 Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects: • As a copper chaperone, GHK-Cu activates superoxide dismutase (SOD), neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protecting against oxidative damage. • It suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1, TNF-α) and NF-κB signaling, reducing inflammation linked to aging and injury. 2.3 Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration: • GHK-Cu promotes angiogenesis by enhancing VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) expression, accelerating blood vessel formation. • It stimulates fibroblast and keratinocyte proliferation, aiding re-epithelialization and ECM remodeling. 2.4 Gene Expression Modulation: • Genomic studies (e.g., Pickart et al., 2012) reveal GHK-Cu resets over 4,000 genes to a youthful state, upregulating repair genes and downregulating inflammatory ones, a unique “epigenetic” effect. Unlike Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 (Pal-GHK), which mimics GHK’s ECM effects, GHK-Cu’s copper component amplifies its regenerative and antioxidant capabilities. 3. Applications 3.1 Anti-Aging: • Wrinkle Reduction: GHK-Cu is applied to reduce fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen and elastin. • Skin Firmness and Texture: It improves elasticity, thickness, and hydration, countering sagging and roughness. • Hyperpigmentation: By inhibiting MMPs and ROS, it may lighten age spots and UV- induced discoloration. 3.2 Wound Healing and Scar Reduction: • GHK-Cu is incorporated into post-surgical gels, burn treatments, and scar creams, accelerating healing and minimizing fibrosis. 3.3 Hair Growth Stimulation: • It promotes hair follicle proliferation and inhibits 5-alpha-reductase (like minoxidil), reducing DHT-related hair loss. 4. Advantages • Broad Bioactivity: GHK-Cu’s effects span ECM synthesis, antioxidation, and regeneration, offering holistic anti-aging and healing benefits. • Natural Origin: As a human plasma component, it aligns with “bio-identical” skincare trends, enhancing consumer trust. • Synergy: Pairs well with vitamin C, hyaluronic acid, or peptides like Pal-GHK for enhanced formulations. • Scientific Backing: Decades of research provide robust evidence of efficacy. 5. Comparison with Alternatives • vs. Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 (Pal-GHK): Pal-GHK enhances penetration but lacks copper’s regenerative boost, making GHK-Cu more potent for healing and antioxidation. • vs. Retinoids: Retinoids excel in cell turnover and pigmentation but are irritating; GHK-Cu is gentler with broader repair benefits. • vs. Ascorbic Acid: Both are antioxidants, but GHK-Cu also stimulates ECM and healing, while vitamin C focuses on collagen synthesis and brightening. • vs. Minoxidil: For hair growth, GHK-Cu offers a milder, multi-action alternative, though minoxidil remains more clinically proven. GHK-Cu stands out as a versatile, biologically active compound with significant potential across various applications. Its ability to modulate gene expression, promote balanced tissue remodeling, and support regenerative processes makes it particularly interesting for wound healing, skin rejuvenation, and potentially neurodegenerative conditions. References 1. Copper Peptide GHK-Cu 2. Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide in the Light of the New Gene Data 3. The human tri-peptide GHK and tissue remodeling 4. Growth-modulating serum tripeptide is glycyl-histidyl-lysine 5. Growth-modulating plasma tripeptide may function by facilitating copper uptake into cells 6. Stimulation of collagen synthesis in fibroblast cultures by the tripeptide-copper complex glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine-Cu2+ 7. Stimulation of sulfated glycosaminoglycan synthesis by the tripeptide-copper complex Glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine-Cu2+ 8. Expression of Glycosaminoglycans and Small Proteoglycans in Wounds: Modulation by theTripeptide–Copper Complex Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine-Cu2+ 9. The interaction of copper(II) and glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine, a growth-modulating tripeptide from plasma. 10. Copper complexes of glycyl-histidyl-lysine and two of its synthetic analogues: chemicalbehaviour and biological activity 11. X-ray and solution structures of Cu(II) GHK and Cu(II) DAHK complexes: influence on theirredox properties 12. The human tripeptide GHK-Cu in prevention of oxidative stress and degenerative conditionsof aging: implications for cognitive health 13. GHK and DNA: Resetting the Human Genome to Health 14. Glycyl-l-histidyl-l-lysine prevents copper- and zinc-induced protein aggregation and centralnervous system cell death in vitro 15. The potential of GHK as an anti-aging peptide |
|
GHK-Cu
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.