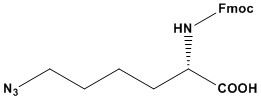
| Synonym: | Fmoc-L-azidolysine |
| CAS #: | 159610-89-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C21H22N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 394.4 |
| Fmoc-Lys(N₃)-OH is a highly versatile and functional amino acid derivative widely used in peptide chemistry and bioorthogonal conjugation strategies. Combining the Fmoc protecting group with an azide-functionalized lysine residue, this compound offers a unique toolkit for both synthetic chemists and biologists. Key Features 1. Fmoc Protecting Group The Fmoc group provides robust protection for the α-amino group of lysine, making it ideal for solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). Its selective removal under mild basic conditions (e.g., with piperidine) allows for iterative peptide elongation without interfering with other functional groups. 2. Azide Functional Group The azide (-N₃) functionality on the lysine side chain adds significant value by enabling site- specific conjugation through click chemistry. This bioorthogonal reaction is highly efficient and allows for precise attachment of various molecular entities, including: Fluorescent probes for imaging applications. Polymers for drug delivery systems. Biologically active ligands or therapeutic agents. 3. Compatibility in SPPS Fmoc-Lys(N₃)-OH is fully compatible with standard SPPS protocols, including those utilizing automated synthesis platforms. The azide group remains stable under typical coupling, deprotection, and cleavage conditions, ensuring a straightforward workflow. Applications 1. Peptide Synthesis Fmoc-Lys(N₃)-OH is indispensable in designing peptides with functional side chains. These modified peptides are useful in studying protein-protein interactions, developing peptide-based therapeutics, and creating biomaterials. 2. Click Chemistry The azide functionality supports copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) and strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC), enabling efficient conjugation without interfering with biological systems. 3. Bioconjugation This compound is a cornerstone in creating hybrid biomolecules, such as peptide-dye conjugates, peptide-drug conjugates, and other functionalized molecules used in diagnostics, imaging, and therapeutics. Strengths 1. High Versatility: The azide group offers a broad range of downstream functionalization opportunities. 2. Stability: The compound is stable under standard SPPS and storage conditions, ensuring reproducibility and efficiency. 3. Ease of Use: Fully compatible with established Fmoc-SPPS workflows and reagents. Limitations 1. Azide Sensitivity: While stable under SPPS conditions, azide groups can be sensitive to reducing environments or high temperatures, necessitating careful handling. 2. Cost: The specialized nature of Fmoc-Lys(N₃)-OH can make it relatively expensive compared to unmodified lysine derivatives. Conclusion Fmoc-Lys(N₃)-OH is an indispensable building block for modern peptide synthesis and bioconjugation. Its dual functionality as an Fmoc-protected amino acid with an azide-modified side chain makes it a valuable tool in chemical biology, materials science, and pharmaceutical research. Despite minor limitations, its versatility and reliability ensure its place as a cornerstone reagent in advanced peptide and protein engineering. References: 1. Click Chemistry 2. Bioorthogonal Chemistry 3. Bioconjugation 4. Fmoc Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis 5. Boc Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis |
|
Fmoc-Lys(N3)-OH
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.