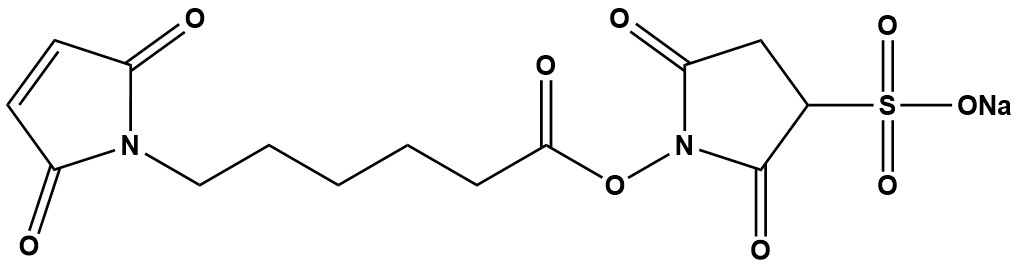
| Synonym: | Sulfo-N-Succinimidyl 6-Maleimidocaproate sodium salt |
| CAS #: | 215312-86-0 |
| Molecular Formula: | C14H15N2NaO9S |
| Molecular Weight: | 410.3 |
| Sulfo-EMCS (CAS 215312-86-0) is a water-soluble, heterobifunctional crosslinking reagent belonging to the same critical family as Sulfo-GMBS and Sulfo-SMCC. It is designed for the stable and efficient conjugation of biomolecules, specifically linking an amine-containing molecule to a thiol-containing molecule. Its primary advantage lies in its longer spacer arm, which provides greater flexibility and reach, making it indispensable for conjugations where steric hindrance is a significant concern. As a heterobifunctional agent, it allows for a controlled, two-step conjugation process. This sequential reaction minimizes the formation of homopolymers (e.g., antibody-antibody aggregates) and unwanted byproducts, leading to higher yields of the desired conjugate. 1. Chemical Structure and Reactive Groups The structure of Sulfo-EMCS consists of three distinct components: • Sulfo-NHS Ester (Amine-Reactive End): This group reacts specifically with primary amines (the ε-amino group of lysine residues or the N-terminus of proteins and peptides) under neutral to slightly alkaline conditions (pH 7.0-8.5). The reaction forms a stable amide bond. The sulfonate (-SO₃⁻) group on the NHS ring confers high water solubility, eliminating the need for organic solvents. • Maleimide Group (Thiol-Reactive End): This group reacts with high specificity and speed with free sulfhydryl groups (-SH) from cysteine residues under neutral pH conditions (pH 6.5-7.5). The reaction forms a stable thioether bond that is irreversible under most biological conditions. • Spacer Arm (ε-Maleimidocaproyl): This is the defining feature of Sulfo-EMCS. The spacer is a 6-carbon (caproyl) chain, which is longer than the 4-carbon (butyryl) chain in Sulfo-GMBS. This results in a total spacer length of approximately 13.6 Å, providing greater spatial separation between the conjugated molecules. Chemical Reaction Summary: • Step 1 (Amine Coupling): Sulfo-EMCS is incubated with the primary amine-containing molecule (e.g., an antibody, carrier protein). The Sulfo-NHS ester forms an amide bond, creating a “maleimide-activated” intermediate. • Purification: Excess, unreacted crosslinker is removed via desalting column or dialysis. This step is critical to prevent self-conjugation in the next step. • Step 2 (Thiol Coupling): The purified maleimide-activated intermediate is mixed with the thiol-containing molecule (e.g., a peptide, a reduced antibody fragment, a cysteine-modified drug). The maleimide group forms a stable thioether bond, completing the conjugation. 2. Key Properties and Characteristics • Solubility: Highly soluble in water and aqueous buffers (PBS, HEPES). This is its primary advantage over the non-sulfonated EMCS, which requires DMSO or DMF for dissolution. • Specificity: High specificity for amines (via NHS-ester) and thiols (via maleimide). This orthogonality allows for precise and predictable conjugation chemistry. • Stability: The lyophilized powder is stable when stored desiccated at ≤ -20°C, protected from light and moisture. In aqueous solution, both reactive groups are hydrolytically labile. The Sulfo-NHS ester half-life is on the order of minutes to hours, and the maleimide group can hydrolyze to a non-reactive maleamic acid. Solutions must be prepared fresh. • Membrane Impermeability: The charged sulfonate group makes Sulfo-EMCS impermeable to cell membranes. This makes it ideal for cell surface labeling and crosslinking extracellular targets without affecting intracellular components. 3. Advantages and Strengths • Long Spacer Arm: The primary advantage of Sulfo-EMCS is its extended 13.6 Å spacer. This is crucial when conjugating large biomolecules (e.g., antibodies to enzymes) where steric hindrance can prevent efficient coupling or impair the function of the conjugated molecules. • Controlled Two-Step Conjugation: The heterobifunctional nature prevents uncontrolled polymerization, leading to more homogeneous and defined conjugates. • Excellent Water Solubility: Simplifies protocols, reduces protein denaturation, and is ideal for sensitive biomolecules that cannot tolerate organic solvents. • High Efficiency: The maleimide-thiol reaction is one of the most efficient in bioconjugation, often proceeding with high yield. • Proven Reliability: A well-established reagent with a long history of successful use in demanding applications like ADC development and immunoassay fabrication. 4. Limitations and Considerations • Hydrolysis Sensitivity: The reactive esters are labile in aqueous solution. Careful timing and immediate use after dissolution are required for optimal efficiency. • Requirement for Free Thiols: The target molecule must possess a free cysteine. If not present, disulfide bonds may need to be reduced (e.g., with TCEP or DTT), which requires an additional step and thorough removal of the reducing agent. • Potential for Maleimide Instability In Vivo: For therapeutic conjugates like ADCs, the thioether bond can be susceptible to retro-Michael addition and thiol exchange with plasma glutathione, potentially leading to premature drug release. (This has led to the development of next-generation reagents). • Spacer Length Trade-off: While the longer spacer reduces steric hindrance, it can also increase non-specific binding or flexibility in the conjugate, which may not be desirable for all applications. 5. Comparison to Related Reagents • vs. Sulfo-GMBS: Sulfo-EMCS has a longer spacer arm (caproyl, ~13.6 Å) compared to Sulfo-GMBS’s butyryl spacer (~10.4 Å). Sulfo-EMCS is preferred when dealing with significant steric hindrance. • vs. Sulfo-SMCC: Sulfo-SMCC is its closest competitor, also featuring a long spacer. However, Sulfo-SMCC has a cyclohexane ring in its spacer, making it more rigid and slightly shorter (~11.6 Å). Sulfo-EMCS has a fully flexible alkyl chain. The choice between a flexible (EMCS) or rigid (SMCC) spacer is often empirical and depends on the specific molecular orientation required. • vs. Sulfo-KMUS: A reagent with an even longer, hydrophilic spacer. Sulfo-EMCS sits in the middle of the spectrum for spacer length. • vs. Homobifunctional Linkers: Superior for creating defined 1:1 conjugates, unlike homobifunctional NHS-esters (e.g., BS³) which create heterogeneous polymers. 6. Typical Applications Sulfo-EMCS is a workhorse in applications where its longer spacer provides a critical advantage: • Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs): Conjugating thiol-containing cytotoxic drugs to lysine residues on monoclonal antibodies. The longer spacer can improve drug accessibility. • Antibody-Oligonucleotide Conjugates: Coupling DNA or RNA to antibodies for diagnostics or targeted delivery. The long spacer helps prevent interference between the large biomolecules. • Enzyme-Labeled Antibodies: Creating immunoconjugates for ELISA or immunohistochemistry where maintaining enzyme activity is paramount. • Hapten-Carrier Protein Conjugation: Covalently linking small peptides (haptens) to large carrier proteins like KLH or BSA to generate immunogens for antibody production. • Immobilization of Proteins: Attaching antibodies or other proteins to thiol-activated surfaces, chips, or beads for biosensors or affinity purification. 7. Storage and Handling • Storage: Store desiccated at -20°C or below. Protect from light. • Solution Preparation: Dissolve in cold, amine-free buffer (e.g., 0.1 M phosphate, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 7.2-7.5) immediately before use. 8. Typical Conjugation Protocol: • Activation: React your amine-containing protein (e.g., 1-2 mg/mL IgG) with a 10-20 fold molar excess of Sulfo-EMCS for 30-60 minutes on ice or at room temperature. • Purification: Immediately purify the reaction mixture using a desalting column (e.g., Zeba™ Spin Column) equilibrated in a conjugation buffer (pH 6.5-7.5) to remove unreacted crosslinker. • Conjugation: Without delay, mix the maleimide-activated protein with the thiol-containing ligand. Incubate for 1-4 hours at room temperature or overnight at 4°C. • Quenching & Storage: Quench the reaction with a slight excess of a low-molecular-weight thiol (e.g., cysteine or 2-mercaptoethanol). Purify the final conjugate and store appropriately. Sulfo-EMCS (CAS 215312-86-0) is a powerful and versatile heterobifunctional crosslinker whose defining characteristic is its extended, flexible spacer arm. It combines the benefits of water solubility, controlled conjugation, and superior reach, making it an excellent choice for challenging conjugations involving large biomolecules where steric hindrance is a primary concern. While it shares the common handling requirements of NHS-maleimide crosslinkers, its proven performance in ADC development, immunoassay design, and protein immobilization solidifies its place as an essential tool in the bioconjugation toolkit. When a longer, more flexible connection is needed, Sulfo-EMCS is often the reagent of choice. |
|
Sulfo-EMCS
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.