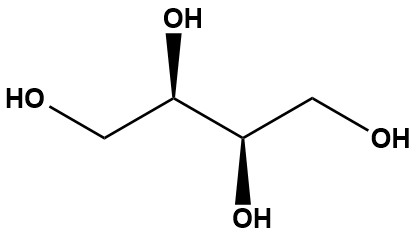
| Synonym: | Threitol; (2R,3R)-Butane-1,2,3,4-tetrol |
| CAS #: | 2418-52-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | C4H10O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 122.1 |
| D-Threitol (CAS #: 2418-52-2), also known by its systematic IUPAC name (2R,3R)-butane-1,2,3,4-tetrol, is a four-carbon sugar alcohol. It is a chiral molecule and exists as an enantiomer of L-Threitol and a diastereomer of Erythritol. While not as well-known as some other sugar alcohols, D-Threitol plays several interesting roles in nature and is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis. 1. Chemical and Physical Properties D-Threitol has the molecular formula C4H10O4 and a molar mass of 122.12 g/mol. It is a white, solid compound with a melting point in the range of 88−90°C. • Structure: As a sugar alcohol (or polyol), its structure is a hydrogenated form of a carbohydrate, where the aldehyde or ketone group has been reduced to a hydroxyl group. It has four hydroxyl groups, making it highly soluble in water. • Chirality: The “D-” prefix indicates its specific stereoisomeric configuration. The presence of two chiral centers gives rise to the D- and L-enantiomers, as well as the achiral diastereomer, Erythritol. • Sweetness: Research has shown that D-Threitol has a sweetness intensity comparable to sucrose, making it a potential candidate for a low-calorie sugar substitute. 2. Natural Occurrence and Biological Role D-Threitol is found in nature in various living organisms, highlighting its biological significance. • Fungi: It is naturally produced by certain fungi, such as the edible fungus Armillaria mellea. Recent research suggests that threitol may act as a signaling molecule for some fungi, promoting their colonization of plant roots. • Insects: In the Alaskan beetle Upis ceramboides, D-Threitol acts as a cryoprotectant or “antifreeze agent,” helping the organism survive in extremely cold environments. • Mammalian Metabolism: D-Threitol has been detected in mammals, including humans. Its presence has been linked to certain metabolic disorders and diseases, such as colorectal cancer and uremia, but its exact role is still a subject of ongoing research. 3. Applications D-Threitol’s unique chemical structure and properties make it valuable in several industries. 3.1 Chemical Synthesis Its primary use is as an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is a precursor for the creation of chiral auxiliaries, which are essential for controlling the stereochemistry of chemical reactions. Its derivatives are used in the synthesis of complex molecules, including carbohydrate and glycoside derivatives. 3.2 Pharmaceuticals • Drug Precursor: D-Threitol is a precursor in the synthesis of certain drugs. For example, it can be used in the synthesis of suxamethonium, an anticancer drug, and tributyrate, another compound used in the development of anticancer therapies. • Antimicrobial Activity: Some research suggests that D-Threitol may possess antimicrobial properties, showing activity against microbes such as E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus. It is also being investigated for its potential to prevent bacteria from attaching to cell walls. 3.3 Food Science • Sugar Substitute: With growing demand for low-calorie sweeteners, D-Threitol is being explored as a potential sucrose replacement. Recent studies on engineered yeast strains have focused on developing efficient biosynthetic methods for its large-scale production. • Packaging: Derivatives of D-Threitol have been used as a component of oxygen-sensitive pigments in “smart plastic films” for food packaging, which can indicate food freshness. D-Threitol is a versatile sugar alcohol with significant applications in synthetic chemistry, biochemical research, and biotechnology. Its natural roles as a fungal metabolite, insect cryoprotectant, and human metabolite underscore its biological importance. Advances in microbial biosynthesis have enhanced its production potential, while its stereochemistry and solubility drive its utility in diverse fields. Continued research into its metabolic pathways, industrial scalability, and clinical relevance will further unlock D-threitol’s potential, cementing its place in science and industry. References: 1. Threitol 2. D-Threitol 3. Threitol 4. D-Threitol |
|
D-Threitol
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.