| Labeled CAS #: | 850080-89-6 |
| Unlabeled CAS #: | 71989-26-9 |
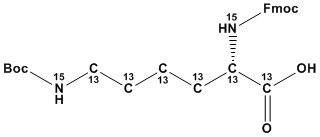
| Molecular Formula: | (13C)6C20H32(15N)2O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 476.5 |
| Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH (¹³C₆,¹⁵N₂) is a specialized, isotopically labeled amino acid derivative crucial for applications in peptide synthesis, particularly within quantitative proteomics and structural biology. This compound integrates stable isotopes (uniformly ¹³C₆ and ¹⁵N 2 labeling) with protective groups (Fmoc for the α-amine and Boc for the amino group side chain), making it indispensable for advanced biochemical studies requiring isotopic tracing. 1. Chemical Structure and Properties: 1.1 Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH (¹³C₆,¹⁵N₂): • The Fmoc (9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl) group serves as a base-labile Nα-protecting group, essential for solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). • The Boc (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) group protects the ε-amino group of lysine, preventing unwanted side reactions during peptide synthesis. • The (¹³C₆,¹⁵N₂) designation specifies that the lysine residue is labeled with six carbon-13 isotopes and two nitrogen-15 isotopes. This isotopic labeling creates a distinct mass shift, which is vital for mass spectrometry-based applications. 1.2 Key Properties: • High purity is critical for accurate quantitative analysis. • Solubility in organic solvents used in SPPS is essential. • Stability under standard SPPS conditions is paramount. • The specific locations of the 13C and 15N isotopes within the lysine molecule are very important for specific applications. 2. Applications: 2.1 Quantitative Proteomics: • This labeled amino acid is extensively used in SILAC (Stable Isotope Labeling by Amino Acids in Cell Culture) and related techniques. • Incorporation of this heavy lysine into peptides and proteins allows for precise quantification of protein expression levels using mass spectrometry. • The mass difference between the labeled and unlabeled (light) lysine-containing peptides enables accurate relative quantification. 2.2 Peptide Synthesis: • It is a key building block in the synthesis of isotopically labeled peptides for various research applications. • The Fmoc/Boc strategy ensures efficient and selective peptide assembly. 2.3 Structural Biology (NMR): • The ¹³C and ¹⁵N labeling makes it valuable for NMR spectroscopy studies of peptide and protein structures. • Isotopic labeling enhances signal dispersion and simplifies spectral analysis. • The specific placement of the isotopes can be chosen to assist in specific NMR techniques. 2.4 Metabolic Studies: • When incorporated into peptides and introduced to biological systems, the labeled Lysine can be used to trace metabolic pathways. 2.5 Pharmaceutical Development: • Isotopic labels are used to track peptide-based pharmaceuticals, and to identify metabolites. Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH (¹³C₆, ¹⁵N₂) is a vital tool for quantitative proteomics, peptide synthesis, and structural biology. Its ability to introduce distinct mass shifts and provide isotopic labels for NMR makes it invaluable for studying protein expression, interactions, and structures. While cost and isotopic purity remain important considerations, ongoing advancements in synthesis and analysis techniques are expanding its applications and accessibility. References Stable Isotope Labeled Amino Acids |
|
Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH (13C6,15N2)
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.