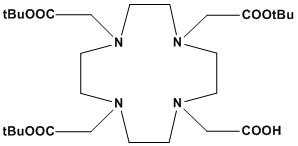
| Synonym: | 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-tris-tert-butyl acetate-10-acetic acid |
| CAS #: | 137076-54-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C28H52N4O8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 572.7 |
| DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester), also known as 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-tris-tert-butyl acetate-10-acetic acid, is a versatile and highly specialized bifunctional chelator in the fields of radiopharmaceutical chemistry, molecular imaging, and targeted radionuclide therapy. It serves as a sophisticated building block, enabling the stable attachment of metal-chelating capabilities to various biomolecules such as peptides, antibodies, and nanoparticles. 1. Chemical Structure and Properties • Core Macrocycle: The heart of DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) is the DOTA macrocycle, which is 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid. This 12-membered cyclic tetraamine framework, adorned with four acetic acid pendant arms, is exceptionally adept at forming highly stable and kinetically inert complexes with a wide array of metal ions, particularly lanthanides and certain transition metals. This robust chelation is crucial for preventing premature dissociation of the radionuclide in vivo. • Protection Strategy: The distinctive feature of DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) is its precisely engineered protection scheme. Three of the four carboxylic acid groups on the acetic acid arms are protected as tert-butyl esters (t-Bu ester). The crucial fourth carboxylic acid group remains unprotected (free). • tert-Butyl Ester Protection: The tert-butyl ester is a well-established acid-labile protecting group. It can be cleanly and efficiently removed under mild acidic conditions (typically using trifluoroacetic acid, TFA). This selective protection is paramount during the synthesis of bioconjugates, as it prevents unwanted side reactions at these carboxylates while allowing for targeted chemical modification at the single free carboxylic acid. • Solubility: Generally exhibits good solubility in common organic solvents such as chloroform, dichloromethane (DCM), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and methanol. This solubility profile is advantageous for its use in various synthetic coupling reactions. • Bifunctional Nature: The combination of a robust metal-chelating macrocyclic core and a precisely positioned, selectively addressable free carboxylic acid (or a derivative like an N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester formed from it) classifies DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) as a bifunctional chelator. This allows it to simultaneously bind a metal ion and covalently attach to a biomolecule, forming a single, targeted molecular entity. 2. Applications DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) is a cornerstone reagent in the development of cutting-edge targeted radiopharmaceuticals and molecular imaging probes, revolutionizing diagnosis and therapy in oncology and other medical fields. 2.1 Radiopharmaceutical Development (Theranostics) • Diagnostic Imaging (PET/SPECT): Its primary role is to chelate a variety of radioactive metal ions for advanced diagnostic imaging techniques such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT). • Theranostics: The unique capability of the DOTA chelator to bind both diagnostic and therapeutic radioisotopes within the same chemical framework facilitates a “theranostic” approach. This allows for personalized medicine, where patients can be imaged to confirm target expression and then treated with a therapeutic radiopharmaceutical based on the same targeting mechanism. 2.2 Bioconjugation • The unprotected carboxylic acid group of DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) serves as the primary attachment point for covalent conjugation with various biomolecules. It can be directly coupled to primary amines (e.g., lysine residues in peptides, proteins, or antibodies) via amide bond formation using standard coupling reagents (e.g., EDC/NHS, HATU, HBTU). It can also be converted into activated esters (like NHS esters) or other reactive derivatives for broader conjugation flexibility. • This bioconjugation allows for the creation of sophisticated targeted delivery systems, where the radionuclide is selectively delivered to cells expressing specific receptors or biomarkers, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy. 2.3 MRI Contrast Agent Precursors • While Gd-DOTA (Dotarem™) is a commercially successful MRI contrast agent, DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) can be used as a precursor for the development of novel Gadolinium-based chelates with potentially improved relaxivity, enhanced targeting capabilities, or unique pharmacokinetic profiles for advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). 2.4 Chemical Synthesis and Ligand Design • DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) acts as a crucial intermediate in the synthesis of more intricate DOTA derivatives. Researchers can further modify the free carboxylic acid, or even the cyclen ring, to incorporate additional functionalities (e.g., PEGylation sites for altered pharmacokinetics, azide or alkyne groups for click chemistry bioconjugation) to fine-tune the properties of the final radioconjugate. 3. Key Advantages • Exceptional Stability: DOTA forms highly thermodynamically stable and kinetically inert complexes with a wide range of metal ions. This prevents premature dissociation of the radionuclide in vivo, which is critical for reducing non-target organ accumulation and enhancing specific delivery to the target site, thereby minimizing toxicity. • Broad Radiometal Compatibility: Its ability to chelate a diverse array of radiometals makes it a versatile platform, adaptable to different imaging modalities (PET, SPECT) and therapeutic strategies (beta-emitters, alpha-emitters). • Bifunctional Design: The clever protection strategy enables the synthesis of highly specific bioconjugates. The unprotected carboxylic acid allows for precise covalent attachment to targeting biomolecules, ensuring specific delivery of the radionuclide. • Controlled Reactivity: The tert-butyl ester protecting groups provide meticulous control over the reactivity of the DOTA core during synthesis. This allows for selective conjugation reactions at the unprotected site before the final deprotection and metal chelation steps, simplifying complex synthetic routes. DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) stands as a foundational molecule in the rapidly evolving landscape of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. Its meticulously designed structure, featuring a highly stable metal-chelating macrocycle and a strategically protected handle for bioconjugation, has profoundly impacted the development of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals. As research continues to refine its synthesis and expand its applications, DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester) remains at the forefront of enabling more precise, personalized, and effective approaches to disease diagnosis and treatment. |
|
DOTA-tris(t-Bu ester)
For Research & Development use only. Not for testing and/or use on humans.